Paper 6: Hierarchical Macro Strategy Model for MOBA Game AI (Honour of Kings)
Abstract
-
RTS games provide partially observable gaming environments, where agents interact with one another in an action space much larger than that of GO.
-
Mastering RTS games requires both strong macro strategies and delicate micro level execution.
-
We propose a novel learning-based Hierarchical Macro Strategy model for mastering MOBA games.
-
Trained by the Hierarchical Macro Strategy model, agents explicitly make macro strategy decisions and further guide their micro level execution.
-
Each of the agents makes independent strategy decisions, while simultaneously communicating with the allies through leveraging a novel imitated cross-agent communication mechanism.
1 Introduction
Game AI aims much more than robots playing games. Rather, games provide ideal environments that simulate the real world. AI researchers can conduct experiments in games, and transfer successful AI ability to the real world.
There are four major aspects that make RTS games much more difficult compared to GO:
-
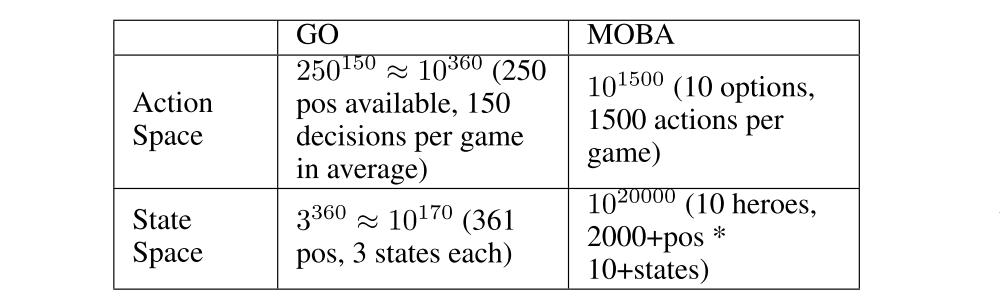
Computational complexity. The computational complexity in terms of action space or state space of RTS games can be up to 10^20000, while the complexity of GO is about 10^250.
-
Multi-agent. Playing RTS games usually involves multiple agents. It is crucial for multiple agents to coordinate and cooporate.
-
Imperfect information. Many RTS games make use of fog of war to increase game uncertainty. When the game map is not fully observable, it is essential to consider gaming among one another.
-
Sparse and delayed rewards. RTS game length could often be larger than 20,000 frames, while each GO game is usually no more than 361 steps.
To master RTS games, players need to have strong skills in both macro strategy operation and micro level execution.
Related work (important here):
-
In recent study, much attention and attempts have been put to micro level execution.
-
So far, OpenAI Five has made the most advanced progress. It was trained directly on micro level action space using PPO algorithms along with team rewards. It has shown strong teamfights skills (强大的团战技巧)and coordination comparable to top professional Dota2 teams.
-
OpenAI’s approach did not explicitly model macro strategy and tried to learn the entire game using micro level play. However, OpenAI Five was not able to defeat professional teams due to weakness in macro strategy management.
-
Related work has also been done in explicit macro strategy operation, mostly focused on
navigation. Navigation aims to provide reasonable destination spots and efficient routes for agents. Most related work in navigation used influence maps or potential field. Providing destination is the most important purpose of navigation in terms of macro strategy operation.The ability to get to the right spots at right time makes essential difference between high level players and the others.Planninghas also been used in macro strategy operation. Although AHTN shows promising results in a mini-RTS game, it suffers from efficiency issue which makes it difficult to apply to full MOBA games directly. -
Previous work in macro strategy failed to provide complete solution:
-
Reasoning macro strategy implicitly by learning upon micro level action space may be too difficult.
-
Previous work on explicit macro strategy heavily relied on handcrafted equations for influence maps/potential fields computation and fusion.
-
One of the most challenging problems in RTS game macro strategy operation is
coordination among multiple agents. Previous work did not consider it in an explicit way. -
We have found that
modeling strategic phase(战略时期划分) is crucial for MOBA game AI performance. Previous work did not consider this.
-
Teaching agents to learn macro strategy operation is challenging. We consider supervised learning to be a better scheme because high quality game replays can be fully leveraged to learn macro strategy along with corresponding execution samples. Note that macro strategy and execution learned using supervised learning can further act as an initial policy for reinforcement learning.
We propose Hierarchical Macro Strategy (HMS) model - a general supervised learning framework for MOBA games such as Dota. HMS directly tackles with computational complexity and multi-agent challenges of MOBA games. More specifically, HMS is a hierarchical model which conducts macro strategy operation by predicting attention on the game map under guidance of game phase modeling. Thereby, HMS reduces computational complexity by incorporating game knowledge. Moreover, each HMS agent conducts learning with a novel mechanism of communication with teammates agents to cope with multi-agent challenge.
2. Introduction to Multiplayer Online Battle Arena (MOBA) Games
2.1 Game Description
As shown in the following figure, Honour of Kings players use left bottom steer button to control movements, while right bottom set of buttons to control skills. Surroundings are observable via the main screen. Players can also learn full map situation via the left top corner mini-map, where observable turrets, creeps, and heroes are displayed as thumbnails. Units are only observable either if they are allies’ units or if they are within a certain distance to allies’ units.
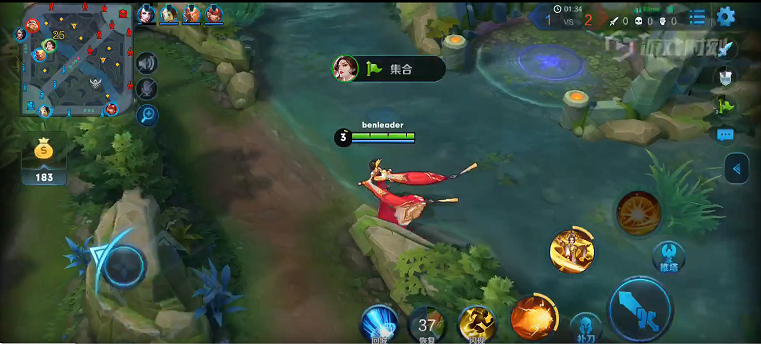
A conceptual map of MOBA is shown in the following figure. To master MOBA games, players need to have both excellent macro strategy operation and proficient micro level execution. Common macro strategies consist of opening(开局), laning(兵线处理), ganking(抓人), ambushing(反蹲), etc. Proficient micro level execution requires high accuracy of control and deep understanding of damage and effects of skills. Both macro strategy operation and micro level execution require mastery of timing to excel, which makes it extremely challenging and interesting.
2.2 Computational Complexity
Action space: The normal game length of Honour of Kings is about 20 minutes, i.e., approximately 20,000 frames in terms of gamecore. At each frame, players make decision with tens of options, including movement button with 24 directions, and a few skill buttons with corresponding releasing position/directions. Even with significant discretization and simplification, as well as reaction time increased to 200ms, the action space is at magnitude of 10^1500.
State space: The resolution of Honour of Kings map is 130,000 by 130,000 pixels, and the diameter of each unit is 1,000. At each frame, each unit may have different status such as hit points, levels, gold. Again, the state space is at magnitude of 10^20000 with significant simplification.
Comparison of action space and state space between MOBA and GO is listed in as below:
2.3 MOBA AI Macro Strategy Architecture
Our motivation of designing MOBA AI macro strategy model was inspired from how human players make strategic decisions. During MOBA games, experienced human players are fully aware of game phases. During each game phase, players pay attention to the game map and make corresponding decision on where to dispatch(派遣) the heroes. During the laning phase players tend to focus more on their own lanes rather than backing up allies, while during mid to late phases, players pay more attention to teamfight spots and pushing enemies’ base.
To sum up, we formulate the macro strategy operation process as “phase recognition -> attention prediction -> execution”. To model this process, we propose a two-layer macro strategy architecture, i.e., phase and attention:
-
Phase layeraims to recognize current game phase so that attention layer can have better sense about where to pay attention to. -
Attention layeraims to predict the best region on game maps to dispatch heroes.
Phase and Attention layers act as high level guidance for micro level execution. The network structure of micro level model is almost identical to the one used in OpenAI Five 1, but in a supervised learning manner. We did minor modification to adapt it to Honour of Kings, such as deleting Teleport.
3 Hierarchical Macro Strategy Model
We propose a Hierarchical Macro Strategy (HMS) model to consider both phase and attention layers in a unified neural network.
3.1 Model Overview
The model takes game features as input. The output consists of two tasks, i.e., attention layer as the main task and phase layer as an auxiliary(辅助的)task. The output of attention layer directly conveys macro strategy embedding to micro level models, while resource layer acts as an axillary task which help refine the shared layers between attention and phase tasks.
The illustrating network structure of HMS is listed in the following figure. HMS takes both image and vector features as input, carrying visual features and global features respectively. In image part, we use convolutional layers. In vector part, we use fully connected layers. The image and vector parts merge in two separate tasks, i.e., attention and phase. Ultimately, attention and phase tasks take input from shared layers through their own layers and output to compute loss.
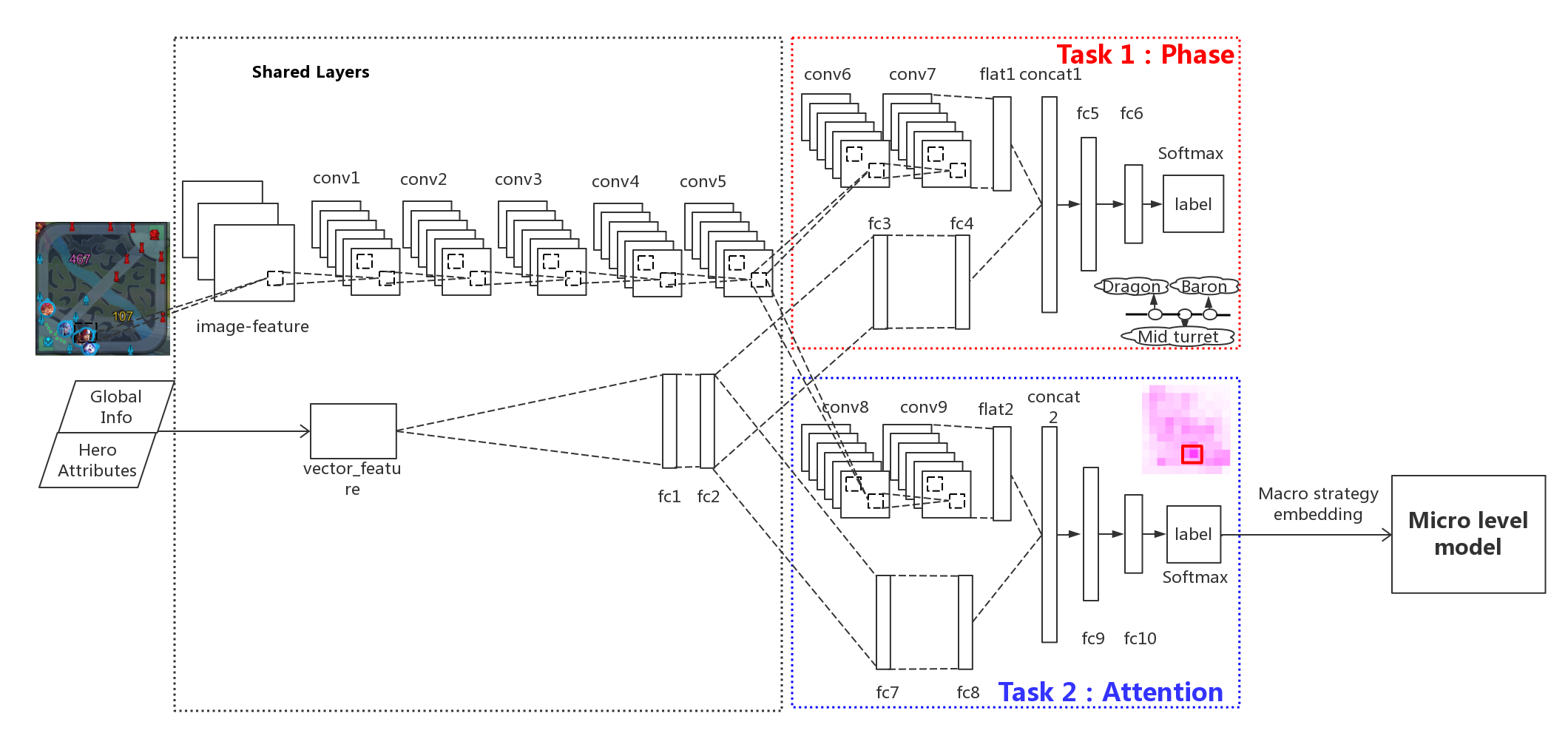
3.2 Attention layer
Similar to how players make decisions according to the game map, attention layer predicts the best region for agents to move to. However, it is tricky to tell from data that where is a player’s destination. We observe that regions where attack takes place can be indicator of players’ destination, because otherwise players would not have spent time on such spots. According to this observation, we define ground-truth regions as the regions where players conduct their next attack. An illustrating example is shown as below.
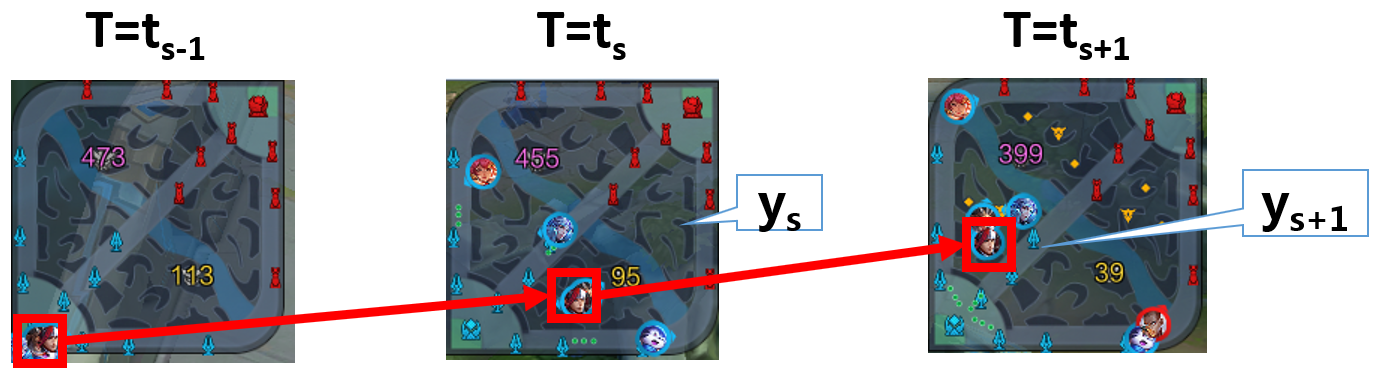
Let s to be one session in a game which contains several frames, and s−1 indicates the session right before s. Let ts to be the starting frame of s. A session ends along with attack behavior, therefore there exists a region ys in ts where the hero conducts attack. The label for s−1 is ys, while label for s is ys+1. By setting up labels in this way, we expect agents to learn to move to ys at the session s-1. Similarly, agents are supposed to move to appropriate regions given game situation.
3.3 Phase layer
Phase layer aims to recognize the current phase. Extracting game phases ground-truth is difficult because phase definition used by human players is abstract. Although roughly correlated to time, phases such as opening, laning, and late game depend on complicated judgment based on current game situation, which makes it difficult to extract ground-truth of game phases from replays. Fortunately, we observe clear correlation between game phases with major resources.
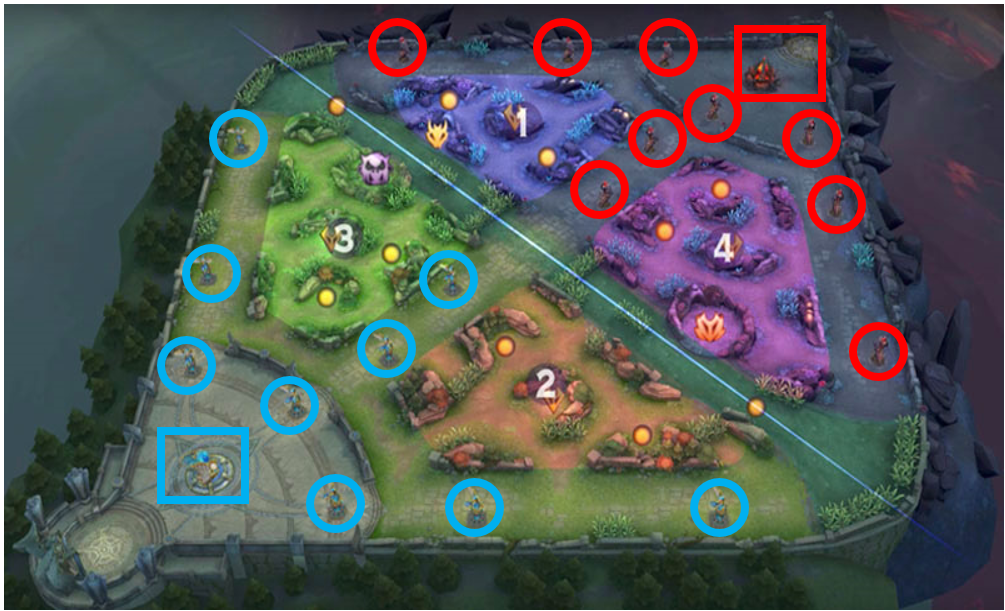
We propose to model phases with respect to major resources. We marked the major resources on the map in the following figure:
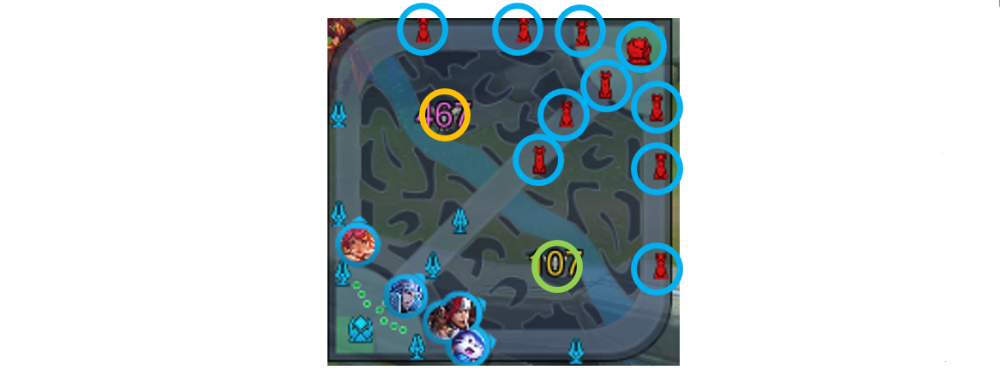
Label definition of phase layer is similar to attention layer. The only difference is that ys in phase layer indicates attack behavior on turrets, baron, dragon, and base instead of in regions. Intuitively, phase layer layer modeling splits the entire game into several phases via modeling which macro resource to take in current phase.
We do not consider other resources such as lane creeps(小兵), heroes, and neutral creeps(野区Buff)as major objectives because usually these resources are for bigger goal, such as destroying turrets or base with higher chance. The following figure shows a series of attack behavior during the bottom outer turret strategy.
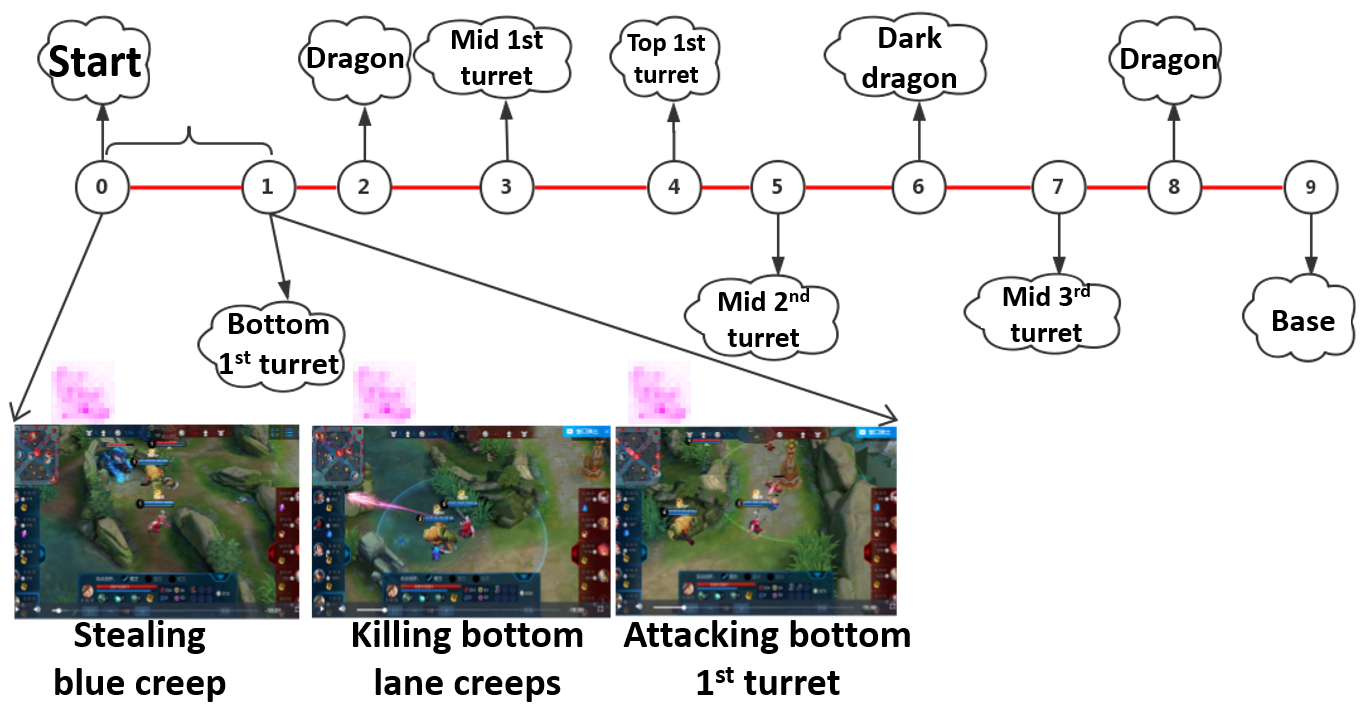
We expect the model to learn when and what major resources to take given game situation, and in the meanwhile learn attention distribution that serve each of the major resources.
3.4 Imitated Cross-agents Communication
Cross-agents communication is essential for a team of agents to cooperate. It is challenging to learn communication using training data in supervised learning because the actual communication is unknown.
To enable agents to communicate in supervised learning setting, we have designed a novel cross-agents communication mechanism. During training phase, we put attention labels of allies as features for training. During testing phase, we put attention prediction of allies as features and make decision correspondingly. In this way, our agents can “communicate” with one another and learn to cooperate upon allies’ decisions. We name this mechanism as Imitated Cross-agents Communication due to its supervised nature.
4 Experiments
4.1 Experimental Setup
Data Preparation: To train a model, we collect around 300 thousand game replays made of King Professional League competition and training records. Finally, 250 million instances were used for training. We consider both visual and attributes features. On visual side, we extract 85 features such as position and hit points of all units and then blur the visual features into 12*12 resolution. On attributes side, we extract 181 features such as roles of heroes, time period of game, hero ID, heroes’ gold and level status and KDA statistics.
Model Setup: We use a mixture of convolutional and fully-connected layers to take inputs from visual and attributes features respectively.
-
On convolutional side, we set five shared convolutional layers, each with 512 channels, padding=1, and one RELU. Each of the tasks has two convolutional layers with exactly the same configuration with shared layers.
-
On fully-connected layers side, we set two shared fully-connected layers with 512 nodes. Each of the tasks has two fully-connected layers with exactly the same configuration with shared layers.
-
Then, we use one concatenation layer and two fully-connected layers to fuse results of convolutional layers and fully-connected layers.
-
We use Adam as the optimizer with base learning rate at 10e-6. Batch size was set at 128. The loss weights of both phase and attention tasks are set at 1.
-
The output for attention layer corresponds to 144 regions of the map, resolution of which is exactly the same as the visual inputs. The output of the phase task corresponds to 14 major resources circled in the figure above.