Paper 9: Hierarchical Reinforcement Learning for Multi-agent MOBA Game (Honour of Kings)
Abstract
-
A novel hierarchical reinforcement learning model for mastering MOBA games.
-
Contributions:
-
Proposing a hierarchical framework, where agents execute macro strategies by imitation learning and carry out micromanipulations(微操)through RL.
-
Developing a simple self-learning method to get better sample efficiency for training.
-
Designing a dense reward function for multi-agent cooperation in the absence of game engine or API.
-
1 Introduction
Compared with Atari, the main challenges of MOBA games for us are:
-
Game engine or API is not available for us. We need toextract features by multi-target detection, and run the game on mobile phones, which is restricated by low computational power. However, the computational complexity can be up to 10^20,000, while AlphaGo is about 10^250. -
Rewards are severely delayed and sparse. The ultimate goal of the game is to destroy the enemies’ crystal, which means that rewards are seriously delayed. Meanwhile, the rewards are really sparse if we set the rewards of −1/1 ac- cording to the final result loss/win. -
Multi-agents’ communication and cooperation are challenging.
This paper is the first attempt to propose reinforcement learning in MOBA game, which does not obtain information from API, but captures information from game video directly.
We cope with the curse of computational complexity through imitation learning of the macro strategies, and it is hard to train for agents because the rewards in this part are severely delayed and sparse.
We develop a distributed platform for sampling to accelerate the training process and combine the A-Star path planning algorithm to do navigation.
The main contributions of this work include:
-
Proposing
a novel hierarchical reinforcement learning framework, which combines imitation learning and reinforcement learning. Imitation learning according to humans’ experience is responsible for macro strategies such as where to go to, when to offend and defend, while reinforcement learning is in charge of micromanipulations such as which skill to release and how to move in battle. -
Developing
a simple self-learning methodwhich learns to compete with agent’s past good decisions and come up with an optimal policy to accelerate the training process. -
Developing a
multi-target detection methodto extract global features composing the state of reinforcement learning. -
Designing
a dense reward functionand usingreal-time data to communicate with each other.
2 Related Work
2.1 RTS Games
Dota2 AI created by OpenAI, named OpenAI Five, has made great success by using PPO algorithm together with well-designed rewards. However, OpenAI Five has used huge computing resources due to lacking of macro strategy.
Related work has also been done in macro strategies by Tencent AI Lab. We have discussed their method in paper 5, it used supervised learning and the training data can be obtained from game replays processed by game engine and API, which run on server. This method is not possible for us because we don’t have access to the game engine or API, and we need to run on mobile phones.
2.2 Hierarchical Reinforcement Learning
Hierarchical reinforcement learning tackles the problem of large state space in environment by decomposing a high dimensional target into several sub-target which is easier to cope with.
2.3 Multi-agent Reinforcement Learning in Games
Multi-agent reinforcement learning (MARL) has certain advantages over single agent learning. Different agents can complete tasks faster and better through knowledge sharing, and there are some challenges as well. For example, the computational complexity increases due to larger state space and action space compared with single agent learning. Because of the above challenges, MARL mainly focuses on stability and adaption.
3 Methods
This section introduces hierarchical architecture, state representation and action definition. Then the network architecture and training algorithm are presented. The reward function design and self-learning method are discussed at last.
3.1 Hierarchical Architecture
The hierarchical architecture is shown in Fig. 1. There are four types of macro actions including attack, move, purchase and adding skill points, which are selected by imitation learning. Then RL algorithm chooses specific action a according to policy π for making micro strategies in state s.
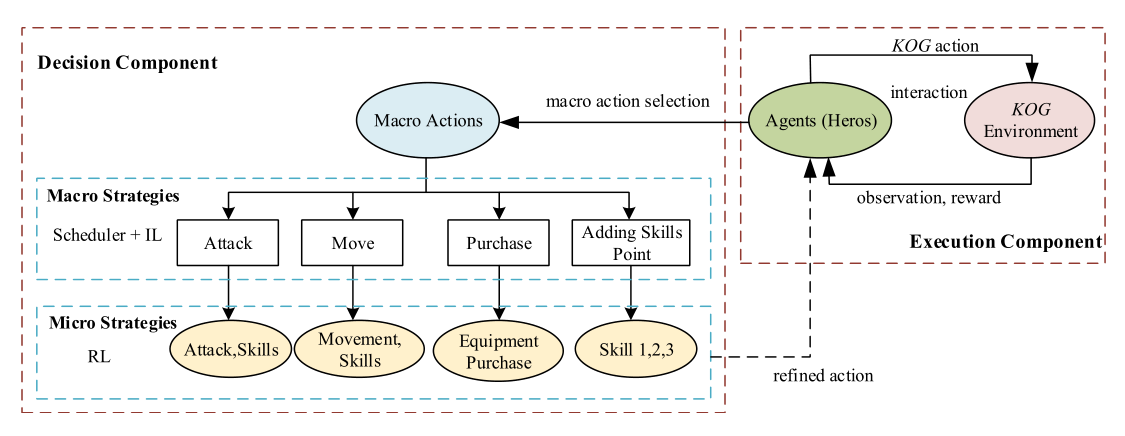
Figure 1: Hierarchical architecture States
The encoded action is performed and the agent can get reward r and next observation s’ from game environment. Rπ is defined as the discounted return. The aim of agents is to learn a policy that maximizes the expected discounted returns, defined as
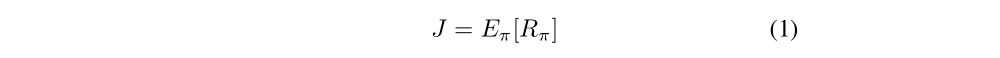
The Scheduler(调度)module designed by observation from game video information is responsible for switching between reinforcement and imitation learning. It is also possible to replace the imitation learning part with high-level expert system for the fact that the data in imitation learning model is produced by high-level expert guidance.
3.2 State Representation and Action Definition
State Representation
It is an open problem on how to represent the state of RTS games optimally. This paper construct a state representation as inputs to neural network from features extracted by multi- target detection, mini-map information of the game, and current view of the agent, which have different dimensions and data types, as illustrated in Fig. 2.
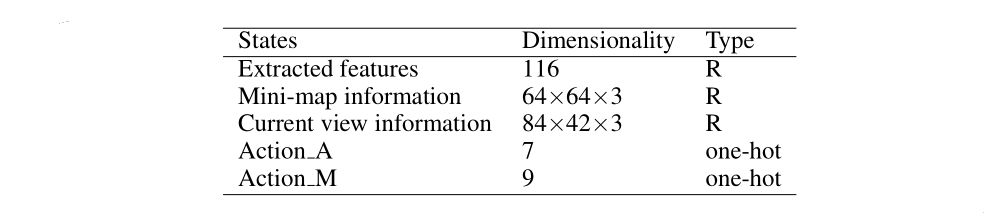
Figure 2: The dimension and data type of our states and action
Extracted features include the position of all heroes, towers, and soldiers, blood volume, gold that the player have and skills released by heroes in the current view, as shown in Fig. 3. All the extracted features are embedded to a 116-dimensional tensor. The inputs at current step are composed of current state information, the last step information, and the last action which has been shown to be useful for the learning process in reinforcement learning. States with real value are normalized to [0, 1].
Action Definition
In this game, we define the action into two parts including Action M and Action A. The motion movement Action M includes Up, Down, Left, Right, Lower-right, Lower-left, Upper-right, Upper-left, and Stay still. When the selected action is attack Action A, it can be Stay still, Skill-1, Skill-2, Skill-3, Attack, and summoned skills(召唤师技能)including Flash and Restore(闪现与治疗). Meanwhile, it is our first choice to attack the weakest enemy when action attack is available for each agent.
3.3 Network Architecture and Training Algorithm Network Architecture
Network Architecture
To tackle the problem of large state space, the micro level algorithm design is similar to PPO algorithm. Inputs of convolutional network are current view and mini-map information with a shape of 84×42×3 and 64×64×3 respectively. Meanwhile, the extracted features consist of 116-dimensional tensors. We use the ReLU activation function in the hidden layer. The output layer’s activation function is softmax function, which outputs the probability of each action.
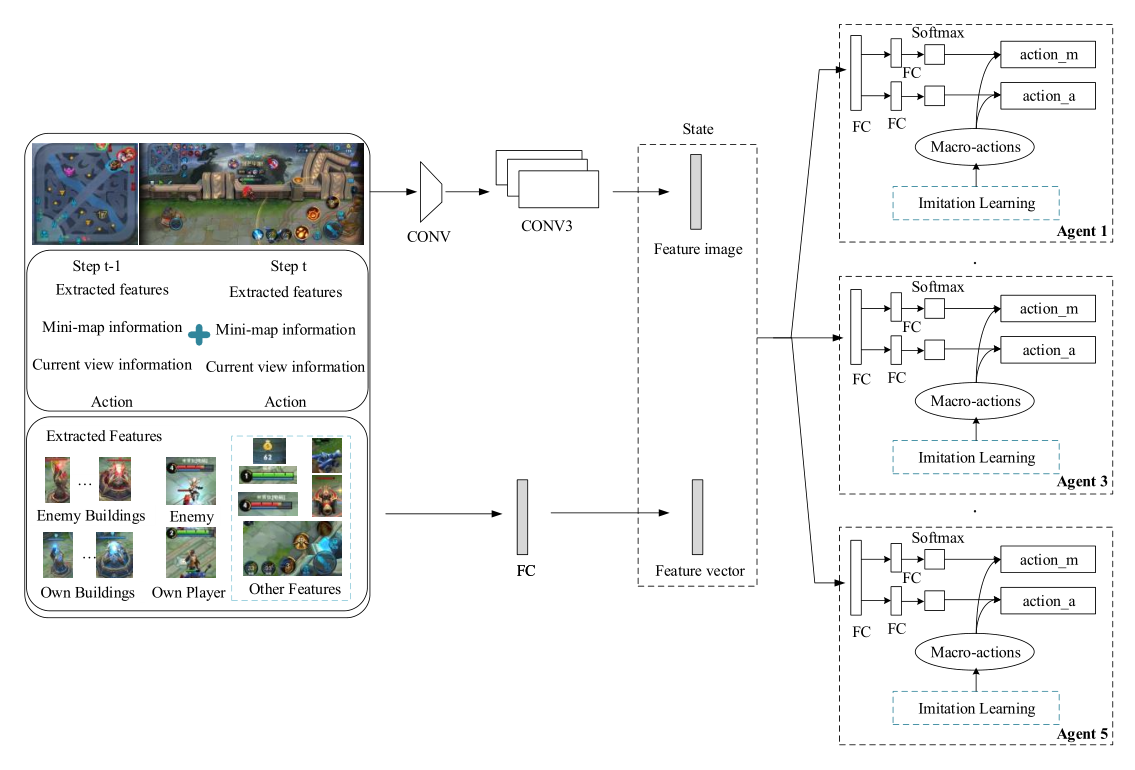
Figure 3: Network architecture of hierarchical reinforcement learning model
Training Algorithm
This paper proposes a Hierarchical Reinforcement Learning (HRL) algorithm for multi-agent learning, and the training process is presented in Algorithm 1. The action probability likelihood is normalized to choose action from macro action At+1. At the end of each iteration, we use the experience replay samples to update parameters of the policy network.

We take the loss of entropy and self-learning into account to encourage exploration in order to balance the trade-off between exploration and exploitation. Loss formula is defined as:
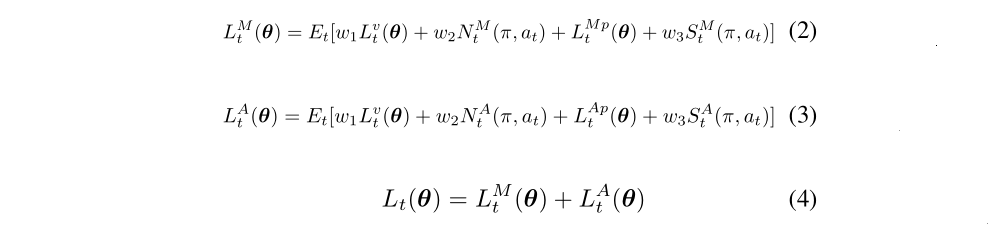
M - action move, A - action attack; w1, w2, w3 are the weights of value loss, entropy loss and self-learning loss that we need to tune. N denotes the entropy loss, S means the self-learning loss. Total loss Lt(θ) is composed of the loss of move and attack for simply computation.
Value loss is defined as
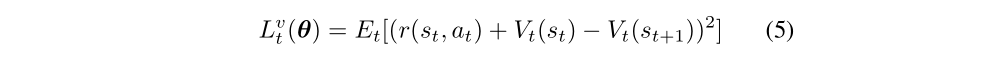
Policy loss of action move is defined as
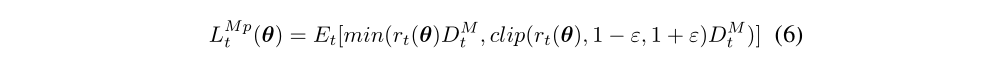
Policy loss of action attack is defined as
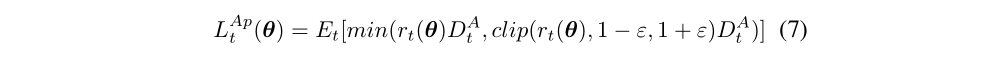
where rt(θ) = πθ(at|st)/πθold(at|st), D denotes the advantage of action computed by the difference between return and value estimation.
3.4 Reward Design and Self-learning
Reward Design
Good learning results of an agent are mainly depending on diverse rewards. Dense reward gives quick positive or negative feedback to the agent, and can help the agents to learn faster and better. Damage amount of an agent is not available for us since we don’t have game engine or API. In our experiment, all agents can receive two parts of rewards including self-reward and global-reward. Self-reward consists of gold and Health Points (HP) loss/gain of the agent, while global-reward includes tower loss and death of allies and enemies.
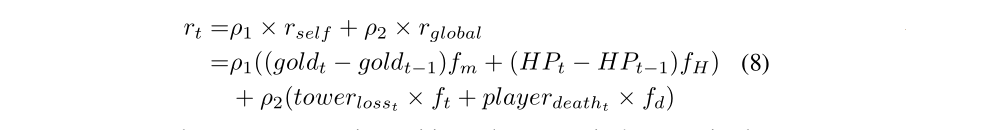
Every term can be positive and negative.
Self Learning
There are many kinds of self-learning methods for RL such as Self-Imitation Learning (SIL) and Episodic Memory Deep Q-Networks (EMDQN). SIL is applicable to actor-critic architecture, while EMDQN combines episodic memory with DQN. However, considering better sample efficiency and easier-to-tune of the system, the proposed method migrates(移植)EMDQN to PPO. Loss of self-learning part can be defined as
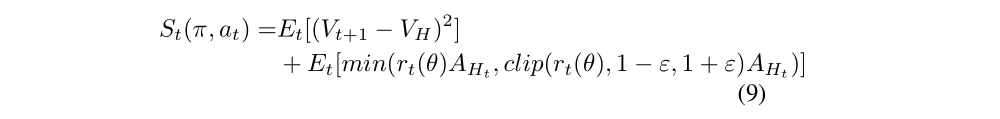
where the memory target VH is the best value from memory buffer, and AHt means the best advantage from it.
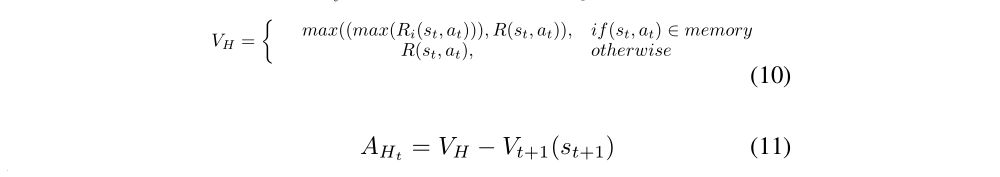
where i ∈ [1,2,· · · ,E], E represents the number of episodes in memory buffer that the agent has experienced.
4 Experiment
We evaluate the performance of our algorithms on two environments: (i) 1v1 map including entry-level, easy-level and medium-level built-in AI, and (ii) a challenging 5v5 map. We analyze the average rewards and win rates during training.
4.1 Setup
The experiment setup includes experiment platform and GPU cluster training platform. In order to increase the diversity and quantity of samples, we use 10 mobile phones for an agent to collect the distributed data. Meanwhile, we need to maintain the consistency of all the distributed mobile phones when training. We transmit the collected sample of all agents to the server and do a centralized training, and share the parameters of network among all agents. Each agent executes its policy based on its own states. As for the features obtained by multi-target detection, its accuracy and category are depicted in Fig. 4, which is adequate for our learning process.
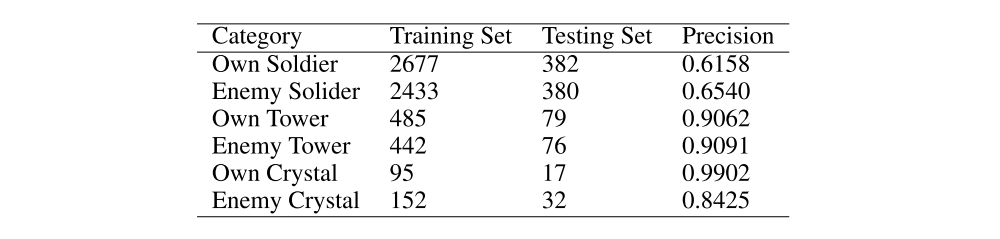
Figure 4: The accuracy of multi-target detection