Concept 9: Deep Reinforcement Learning for Trading (2)
本文紧接前文记录 Denny Britz 更 high-level 地使用强化学习技术赋能可盈利的算法交易系统的经验。
Trading as Multi-agent Problem
Efficient Market Hypothesis(有效市场假说)is just a theoretical model, we can build profitable systems that consistently beat the market. Will the market eventually adjust and take away that opportunity? Probably, but that’s irrelevant, because the market may take months, years or decades to adjust (just look at HFT 高频交易), and you are free to evolve your system over time, looking for new opportunities and adjusting to the adjusting market yourself. The market may have adjusted to your system as profits started decreasing, but it took more than 12 months, and with the right motivation you probably could have adjusted and improved the system to work again.
Rather than thinking about markets from an economics perspective, we prefer to think about them from a Game Theory or Reinforcement Learning perspective.
The market does not exist.
What people call the market is an emergent property of many agents acting in an environment trying to maximize their own objective. The objective may be slightly different for everyone. Some want to sell shares they obtained through a stock options plan(股票期权计划)at a good price. Some engage in arbitrage(套利)for quick profits. Some try to predict short-term movements based on news or charting patterns. Some engage long-term speculation based on fundamentals. Some are designated market makers providing liquidity for a specific asset or exchange in return for a fee. Each could be a human acting on gut feeling and emotion, a human following some kind of implicit fuzzy algorithm (e.g. charting), or an automated system acting on data. The combined behavior of all these agents gives rise to this illusive thing that people call the market. Your goal isn’t to beat the market, it’s to beat some of the other players in the market over a time horizon you care about. The time horizon part is important. Not every trade has a clear winner and loser, because agents are optimizing over different time horizons, ranging from microseconds to decades.
A trader’s mindset: It’s all relative
If you come from a tech or startup background, transitioning to trading may require a change in thinking. Products and engineering are often about absolutes. If your website takes 100ms to load that’s pretty good. Making it load in 99ms provides negligible benefit to the end-user. It’d be a waste of engineering resources. The same is true for startups. Paul Graham likes to say that startups are rarely killed by competitors. Rather, they commit suicide. They fail because they cannot find customers, don’t have a solid business model, or because of founder issues. Being killed by competition with a slightly better product is quite rare.
Trading is different. It’s about relatives. It’s fine if your website takes a horrible 10 seconds to load if your competitor needs 11 seconds. Having crappy data is fine if everyone else’s data is even crappier. Paying high trading fees is fine if everyone is paying the same. This is pretty obvious if you look at the market as a multi-player game. Even if you’re a bad player on an absolute scale, you can win if your competition is worse. This has direct effects on how you build software to trade in the markets.
Building Trading Infrastructure
What a focus on relative performance means for engineering can be quite counterintuitive.
When building infrastructure for a product-based company you would prefer using battle-tested, robust frameworks that minimize risk. Why re-invent the wheel if someone else has already built it? It’s safe to use something that has been adopted by thousands of people. This is where open source shines. But when you are building trading infrastructure, you should think twice about this.
Widely adopted technologies are commodities(日用品). If you use the same technologies as everyone else, where will your advantage come from? When building a product this doesn’t matter because it’s about absolute SLAs. But trading is about relatives.
Each commoditized technology you can specialize and build yourself is an opportunity to beat the competition.
By being hybrid cloud you can reduce latencies. By storing data in an efficient binary format you can save serialization time, leading to faster iteration during development, and faster predictions in production. By creating custom integrations with exchanges instead of using off-the-shelf APIs you may be able to use specific order types that are not available to others, or gain an informational advantage by processing exchange-specific information. And so on. Building highly-specialized non-generic systems is what engineers hate. We love generalization and abstraction. But specialization is often where your advantage in trading comes from.
You don’t need to start from scratch and implement your own programming language to start trading. But you should be aware of the tradeoffs you are making when adopting commoditized technologies. Make conscious decisions about it. Some of the things above seem minor - but a large number of tiny advantages can add up to a significant edge.
AI and Trading
You may say, I really don’t want to compete on the infrastructure side. Instead, I want to build a smarter model that makes better predictions. I’ve heard this a LOT, but I’ve never seen it work.
AI is pretty commoditized. I would say it’s more commoditized than excellent infrastructure engineering, data collection, or inductive biases from domain knowledge. These days, you can easily download SOTA models and run them on your data. Unless you are at the forefront of some extremely relevant research, it’s unlikely that you can gain a significant edge just from training a better model.
When people realize that their fancy AI model built on crappy infrastructure trained with crappy data (that’s also used by everyone else) doesn’t work, they give up. AI can give you an edge, but not an edge so huge that it allows you to ignore other factors. You still need to build good infrastructure, get good data, have decent latencies, and so on. Few people seem to be willing to spend time on these unsexy things. Think of each as a multiplier. If one is close to zero, it doesn’t matter how good your AI model is.
So, what are some these other things?
-
Market - Pick the right market(s) to trade in. Don’t go for the obvious choices that everyone is picking by default. The harder it is to get access to a market, both legally and technically, the more likely that you will find opportunities. Less liquid markets may be overlooked by sophisticated funds because they don’t scale to their AUM(资产管理规模). Again, this is often counterintuitive to engineers who go for “good APIs” - good APIs typically mean popular. Popular typically means commoditized.
-
Data - Think about data sources that others do not have access to, or are not willing to get. For example, there may be data that’s difficult to crawl due to sophisticated rate restrictions IP bans. Most people will give up here. This is an opportunity for you. Be skeptical of popular APIs and open source software. It’s the same data that everyone else uses.
-
Latencies - You’re probably not planning to compete with HFT traders (bad idea), but that doesn’t mean you can completely ignore latencies. Better latencies will probably lead to easier execution with less slippage. Be careful about where you host your systems, how you send data around, how you serialize data, and so on.
-
Models - In general, better data is more important than better models, but better models can also give you an edge. Note that you are often trading off model complexity with latencies.
-
Execution - A good model doesn’t mean much if you can’t execute. Historical data you collect may look quite different from what’s actually happening on the exchange. You are not going to know until you start live trading.
Trading with Reinforcement Learning
RL is the right approach to trading in the markets. However, a lot of tricks are necessary to make it work. The main benefit of RL is that you don’t need to set up a differentiable loss function. Instead, you can directly optimize Profit and Loss over some time horizon. By building a good simulation, your model can learn to be robust to latencies, jitter(颤动), slippages(滑移), and other things that may happen in a real market.
With supervised learning, it’s a lot harder. There are many hyperparameters you would need to get “just right” - What time horizon to optimize over? What to optimize (log returns? For what position size(持仓规模)?)? When to exit a position? How to deal with stochasticity arising from latencies, rejected orders, API issues, etc? How to deal with non-iid data? And so on. I’m sure you can make that work if you try really hard, but relying on simulation-based approached just seems like a more principled solution.
I also believe that market simulations are a pretty good testbed for RL. They have a few properties that many of today’s techniques struggle with:
-
Sparse positive feedback. With random exploration and naive rewards, you are quite unlikely to discover good policies.
-
Requires generalization to future dates. Generalization is often overlooked in RL where researchers “test on the training set”.
-
With a good simulator, environments can provide a lot of stochasticity in the form of from latencies, jitter, API issues, slippage, etc.
-
Nonstationarity. The market data distribution changes over time, and the agent must learn to deal with it.
-
A low signal to noise ratio(信噪比)in the observations.
Optimizing for Iteration Speed
Most inefficiencies are fleeting as other agents will adapt to your strategies. How fleeting? It depends. Depending on where and how you are trading, they could last milliseconds, seconds, minutes, hours, days, weeks, or months.
The way to be consistently profitable is to become consistently good at identifying fleeting opportunities.
This is basically meta-learning.
Optimize the speed of your outer loop when training models. The faster you can iterate on discovering new strategies and adapting your models and infrastructure, the better. Build your infrastructure around this. Querying and loading bulk historical data to play around with should be as fast as possible. Pay special attention to deserialization costs. When building a market simulator with matching engine, benchmark it extensively. Minimize RPC and network round trips. We’re talking about orders of magnitude here. The first simulator could be about 50x slower than the most recent one. Since the model is trained in simulation, that means 50x faster iteration speed when training or playing around. Automate data visualization so that you can look at them easily when you get unexpected results.
You can’t make money when the market goes down?
A common argument and misconception is that I was lucky and made profits because the market was going up. Actually, many months PnL graph looked something like this:
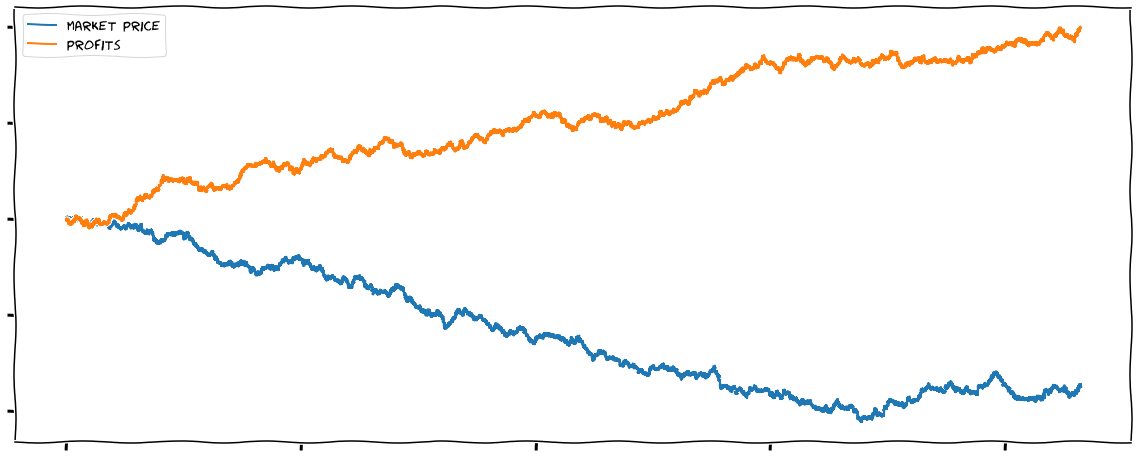
This was not because of shorting(做空)the asset. Shorting was not possible in some market.
There is rarely such thing as the market going down all the time.