Paper 54: FinRL: A Deep Reinforcement Learning Library for Automated Stock Trading in Quantitative Finance
Github: https://github.com/AI4Finance-LLC/FinRL-Library.
Abstract
-
We introduce a DRL library FinRL that facilitates beginners to expose themselves to quantitative finance and to develop their own stock trading strategies. Along with easily-reproducible tutorials, FinRL library allows users to streamline their own developments and to compare with existing schemes easily.
-
Within FinRL, virtual environments are configured with stock market datasets, trading agents are trained with neural networks, and extensive backtesting is analyzed via trading performance. Moreover, it incorporates important trading constraints such as transaction cost, market liquidity and the investor’s degree of risk-aversion.
-
FinRL is featured with completeness, hands-on tutorial and reproducibility that favors beginners:
-
at multiple levels of time granularity, FinRL simulates trading environments across various stock markets, including NASDAQ-100, DJIA, S&P 500, HSI, SSE 50, and CSI 300;
-
organized in a layered architecture with modular structure, FinRL provides fine-tuned SOTA DRL algorithms (DQN, DDPG, PPO, SAC, A2C, TD3, etc.), commonly used reward functions and standard evaluation baselines to alleviate the debugging workloads and promote the reproducibility;
-
being highly extendable, FinRL reserves a complete set of user-import interfaces.
-
-
We incorporated three application demonstrations, namely single stock trading, multiple stock trading, and portfolio allocation.
1 Introduction
DRL framework provides two major advantages - portfolio scalability and market model independence. Taking many complex financial factors into account, DRL trading agents build a multi-factor model and provide algorithmic trading strategies, which are difficult for human traders.
To implement a DRL or RL driven trading strategy is nowhere near as easy. The development and debugging processes are arduous(费力的)and error-prone(易出错的). Training environments, managing intermediate trading states, organizing training-related data and standardizing outputs for evaluation metrics - these steps are standard in implementation yet time-consuming especially for beginners. Therefore, we come up with a beginner-friendly library with fine-tuned standard DRL algorithms. It has been developed under three primary principles:
-
Completeness (cover components of the DRL framework completely)
-
Hands-on tutorials
-
Reproducibility
FinRL provides common building blocks that allow strategy builders to configure stock market datasets as virtual environments, to train DNNs as trading agents, to analyze trading performance via extensive backtesting, and to incorporate important market frictions. In this paper, we present a three-layered FinRL library that streamlines the development stock trading strategies.
-
On the lowest level is environment, which simulates the financial market environment using actual historical data from six major indices with various environment attributes such as closing price, shares, trading volume, technical indicators etc.
-
In the middle is the agent layer that provides fine-tuned standard DRL algorithms (DQN, DDPG, Adaptive DDPG, Multi-Agent DDPG, PPO, SAC, A2C and TD3, etc.), commonly used reward functions and standard evaluation baselines to alleviate the debugging workloads and promote the reproducibility. The agent interacts with the environment through properly defined reward functions on the state space and action space.
-
The top layer includes applications in automated stock trading, where we demonstrate three use cases, namely single stock trading, multiple stock trading and portfolio allocation.
The contributions of this paper are summarized as follows:
-
FinRL is an open source library specifically designed and implemented for quantitative finance. Trading environments incorporating market frictions are used and provided.
-
Trading tasks accompanied by hands-on tutorials with built-in DRL agents are available in a beginner-friendly and reproducible fashion using Jupyter notebook. Customization of trading time steps is feasible.
-
FinRL has good scalability, with a broad range of fine-tuned SOTA DRL algorithms. Adjusting the implementations to the rapid changing stock market is well supported.
-
Typical use cases are selected and used to establish a benchmark for the quantitative finance community. Standard backtesting and evaluation metrics are also provided for easy and effective performance evaluation.
3 The Proposed FinRL Library
3.1 Architecture of the FinRL Library
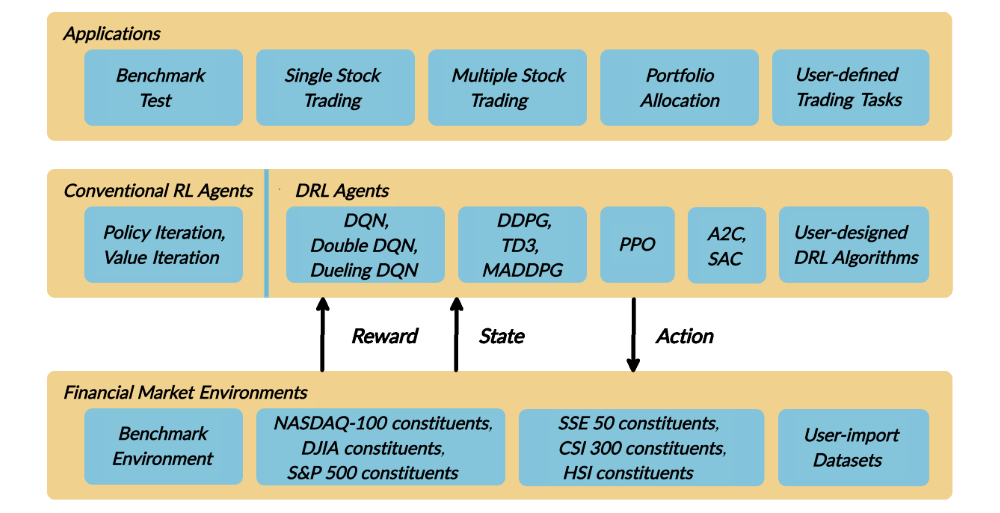
Figure 1: An overviewof our FinRL library.
The architecture of the FinRL library is shown in Figure 1, and its features are summarized as follows:
-
Three-layer architecture: The three layers of FinRL library are stock market environment, DRL trading agent, and stock trading applications. The agent layer interacts with the environment layer in an exploration-exploitation manner, whether to repeat prior working-well decisions or to make new actions hoping to get greater rewards. The lower layer provides APIs for the upper layer, making the lower layer transparent to the upper layer.
-
Modularity: Each layer includes several modules and each module defines a separate function. One can select certain modules from any layer to implement his/her stock trading task. Furthermore, updating existing modules is possible.
-
Simplicity, Applicability and Extendibility: Specifically designed for automated stock trading, FinRL presents DRL algorithms as modules. In this way, FinRL is made accessible yet not demanding. FinRL provides three trading tasks as use cases that can be easily reproduced. Each layer includes reserved interfaces that allow users to develop new modules.
-
Better Market Environment Modeling: We build a trading simulator that replicates live stock market and provides backtesting support that incorporates important market frictions such as transaction cost, market liquidity and the investor’s degree of risk-aversion. All of those are crucial among key determinants of net returns.
3.2 Environment: Time-driven Trading Simulator
Our trading environments, based on OpenAI Gym framework, simulate live stock markets with real market data according to the principle of time-driven simulation. FinRL library strives to provide trading environments constructed by six datasets across five stock exchanges.
-
State Space, Action Space, and Reward Function
-
State space S
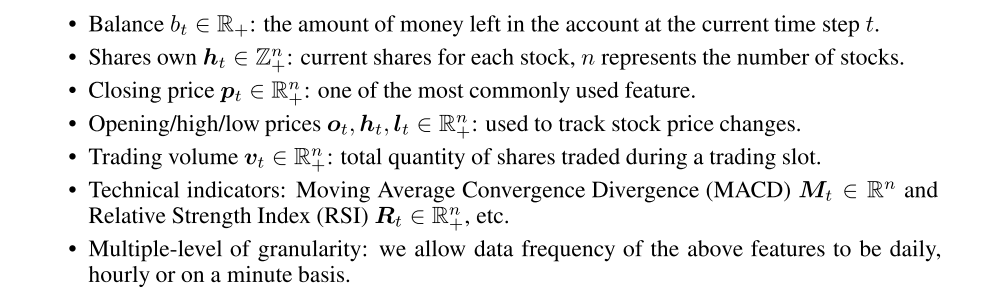
-
Action space A
Normally, a ∈ A includes three actions: a ∈ {−1, 0, 1}, where −1, 0, 1 represent selling, holding, and buying one stock. Also, an action can be carried upon multiple shares. We use an action space {−k, …, −1, 0, 1, …, k}, where k denotes the number of shares. For example, “Buy 10 shares of AAPL” or “Sell 10 shares of AAPL” are 10 or −10, respectively.
-
Reward function

-
-
Standard and User Import Datasets
Various finance markets require different DRL algorithms to get the most appropriate automated trading agent. Realizing that setting up training environment is a time-consuming and laborious work, FinRL provides six environments based on representative listings, including NASDAQ-100, DJIA, S&P 500, SSE 50, CSI 300, and HSI, plus one user-defined environment. With those efforts, this library frees users from tedious and time-consuming data pre-processing workload.
We are well aware that users may want to train trading agents on their own data sets. FinRL library provides convenient support to user imported data to adjust the granularity of time steps. We specify the format of the data for each of the use cases. Users only need to pre-process their data sets according to our data format instructions.
3.3 Deep Reinforcement Learning Agents
FinRL library includes fine-tuned standard DRL algorithms, namely, DQN, DDPG, Multi-Agent DDPG, PPO, SAC, A2C and TD3. We also allow users to design their own DRL algorithms by adapting these DRL algorithms, e.g., Adaptive DDPG, or employing ensemble methods. The comparison of DRL algorithms is shown in Figure 2:
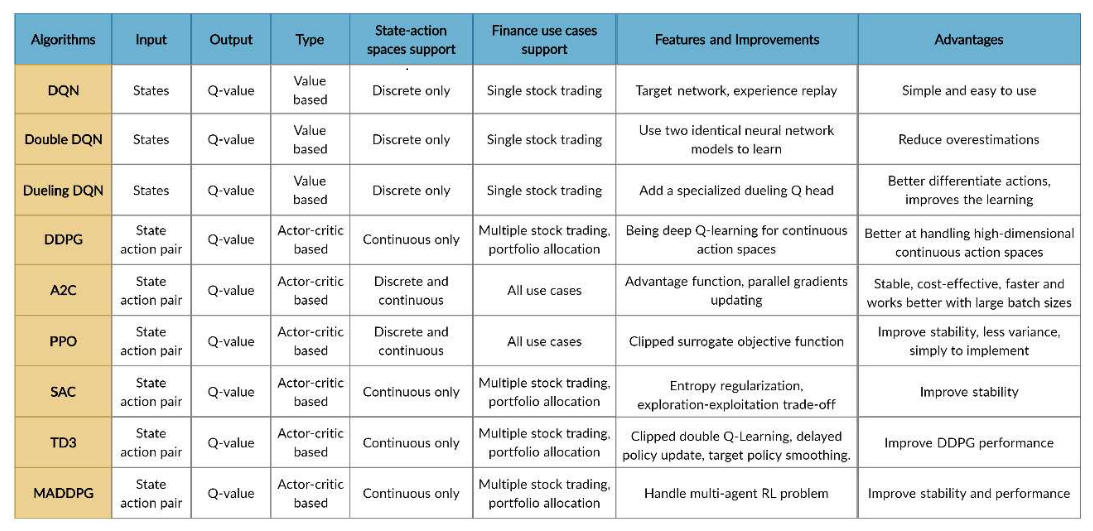
Figure 2: Comparison of DRL algorithms.
The implementation of the DRL algorithms are based on OpenAI Baselines and Stable Baselines.
4 Evaluation of Trading Performance
Standard metrics and baseline trading strategies are provided to support trading performance analysis. FinRL library follows a training-validation(校验)-testing flow to design a trading strategy.
4.1 Standard Performance Metrics
FinRL provides five evaluation metrics to help users evaluate the stock trading performance directly, which are final portfolio value, annualized return, annualized standard deviation, maximum draw-down ratio, and Sharpe ratio.
4.2 Baseline Trading Strategies
Baseline trading strategies should be well-chosen and follow industrial standards. The strategies will be universal to measure, standard to compare with, and easy to implement. In FinRL library, traditional trading strategies serve as the baseline for comparing with DRL strategies. Investors usually have two objectives for their decisions: the highest possible profits and the lowest possible risks of uncertainty. FinRL uses five conventional strategies, namely passive buy-and-hold trading strategy, mean-variance strategy, and min-variance strategy, momentum trading strategy, and equal-weighted strategy to address these two mutually limiting objectives and the industrial standards.
4.3 Training-Validation-Testing Flow
With our use cases as instances, the stock market data are divided into three phases in Figure 3. Training dataset is the sample of data to fit the DRL model. The model sees and learns from the training dataset. Validation dataset is used for parameter tuning and to avoid overfitting. Testing (trading) dataset is the sample of data to provide an unbiased evaluation of a fine-tuned model. Rolling window is usually associated with the training-validation-testing flow in stock trading because investors and portfolio managers may need to rebalance the portfolio and retrain the model periodically. FinRL provides flexible rolling window selection such as on a daily basis, monthly, quarterly, yearly or by user specified.
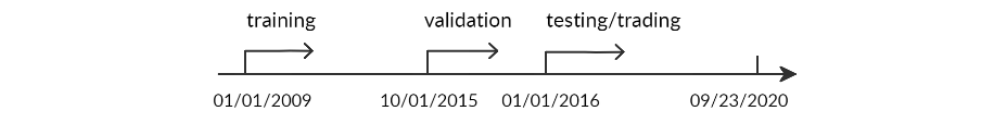
Figure 3: Data splitting.
4.4 Backtesting with Trading Constraints
In order to better simulate practical trading, we incorporate trading constraints, risk-aversion and automated backtesting tools.
-
Automated Backtesting. It reduces the human error. In FinRL library, we use the
Quantopian pyfolio packageto backtest our trading strategies. This package is easy to use and consists of various individual plots that provide a comprehensive image of the performance of a trading strategy. -
Incorporating Trading Constraints. Transaction costs incur when executing a trade. There are many types of transaction costs, such as broker commissions and SEC fee. We allow users to
treat transaction costs as a parameter in our environments:-
Flat fee: a fixed dollar amount per trade regardless of how many shares traded.
-
Per share percentage: a per share rate for every share traded, for example, 1/1000 or 2/1000 are the most commonly used transaction cost rate for each trade.
Moreover, we need to consider
market liquidityfor stock trading, such as bid-ask spread(买卖价差). Bid-ask spread is the difference between the prices quoted for an immediate selling action and an immediate buying action for stocks. In our environments, we canadd the bid-ask spread as a parameter to the stock closing price to simulate real world trading experience. -
-
Risk-aversion. It influences one’s trading strategy when facing different market volatility level. To control the risk in a worst-case scenario, such as financial crisis of 2007–2008, FinRL
employs the financial turbulence indexthat measures extreme asset price fluctuation: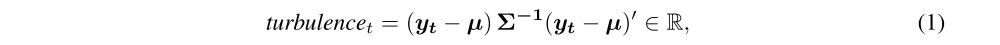
where yt denotes the stock returns for current period t, µ denotes the average of historical returns, and Σ denotes the covariance of historical returns. It is used as
a parameter that controls buying or selling action, for example if the turbulence index reaches a pre-defined threshold, the agent will halt buying action and starts selling the holding shares gradually.